- Cisco Community
- Technology and Support
- Networking
- Routing
- Re: Nat using network address?
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Nat using network address?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-18-2010
05:29 AM
- last edited on
03-25-2019
03:30 PM
by
ciscomoderator
![]()
Hi
I have found the attached pdf in cisco documentation for CCNA4 Exploration. I don't understand how can this be right. How can I use the network or broadcast address for nat mapping? Please explain me how this works.
- Labels:
-
Other Routing
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-18-2010 08:42 AM
Hi,
1. ACL is defining which sourced traffic can be NAT translated.
2. ip nat pool defines local global addresses.
So, Traffic sourced from 192.168.10.0/24, 192.168.20/24, and 192.168.30.0/24 will be local inside addresses and will be translated to one of local global address of NAT pool in "209.165.202.128" ~ "130".
It is is PAT with overload command.
NAT will start use TCP/UDP available ports with 209.165.202.128 and move to 209.165.202.129 after it consumes all available ports of 209.165.202.128.
R2(config)#ip access-list standard R2NAT
R2(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
R2(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.20.0 0.0.0.255
R2(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255
R2(config)#ip nat pool R2POOL 209.165.202.128 209.165.202.130 netmask 255.255.255.252
R2(config)#ip nat inside source list R2NAT pool R2POOL overload
KK
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-18-2010 10:06 AM
Well it's not quite like this. On Gns it starts translating at .129 and only uses .129 and .130. This was my actual problem 209.165.202.128/30 is a network address not a valid ip address. so how can nat translate into a network address?
If I force a static NAT using .128 it actually works. I don't understand why but it seems that the ip route command (ISP(config)#ip route 209.165.202.128 255.255.255.224 serial0/0/0 from that pdf) doesn't care if the routed ip address is a network/broadcast ip.
It seems that from a /30 range I can use not two but all 4 addresses if I use 2 static translations. Am I correct?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
08-18-2010 11:26 AM
Hi,
By default, "ip classless" is configured on IOS router and not shown from sh run.
With ip classless enabled, you can use all 4 IP on /30 subnet. (or, you can say all IP address in any subnet.)
Here is a good document about it.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/11_3/np1/configuration/guide/1cipadr.html#wp1404
Enable Classless Routing Behavior
At times, a router might receive packets destined for a subnet of a network that has no network default route. http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/11_3/np1/configuration/guide/1cipadr.html#wp1413shows a router in network 128.20.0.0 connected to subnets 128.20.1.0, 128.20.2.0, and 128.20.3.0. Suppose the host sends a packet to 128.20.4.1. By default, if the router receives a packet destined for a subnet it does not recognize, the router discards the packet.
Figure 2 No IP Classless Routing
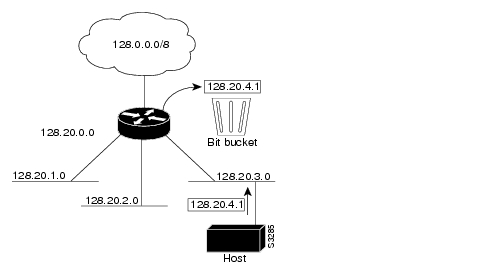
In http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/11_3/np1/configuration/guide/1cipadr.html#wp9195, classless routing is enabled in the router. Therefore, when the host sends a packet to 128.20.4.1, instead of discarding the packet, the router forwards the packet to the best supernet route.
Figure 3 IP Classless Routing

To have the Cisco IOS software forward packets destined for unrecognized subnets to the best supernet route possible, perform the following task in global configuration mode:
Discover and save your favorite ideas. Come back to expert answers, step-by-step guides, recent topics, and more.
New here? Get started with these tips. How to use Community New member guide
